Understanding Rashes Linked to Liver Disease

Intro
Rash presentations related to liver disease represent an important connection between dermatological symptoms and underlying systemic conditions. Recognizing these rashes can assist health professionals in diagnosing liver issues early. In this article, we examine the different types of liver diseases and their associated dermatological manifestations. Furthermore, we discuss diagnostic methods and treatment options available for these conditions. Understanding the connection between liver function and skin health allows for a more holistic approach to patient care.
Methodologies
Description of Research Techniques
Research into the rashes associated with liver disease incorporates various methodologies. Clinical observations, case studies, and systematic reviews all play a role in compounding knowledge. By analyzing patient records, researchers gather data on the types of rashes observed in liver disease sufferers. Moreover, interviews with healthcare professionals provide insight into the clinical practices related to these symptoms.
Tools and Technologies Used
Several tools support the identification and analysis of rashes related to liver disease. Dermatological examination techniques such as dermoscopy provide significant detail on skin lesions. Imaging technologies may also be used to assess liver health, including ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Discussion
Comparison with Previous Research
Previous studies have highlighted common rashes linked to liver dysfunction, such as pruritus and xanthomas. These studies often emphasize the need for a multi-disciplinary approach, incorporating both dermatology and hepatology. Newer research builds upon this foundation, further exploring the biochemical pathways that connect liver function to skin health. Modern findings delve deeper into the immune response, shedding light on how liver conditions may precipitate skin issues.
Theoretical Implications
The theoretical implications of understanding these connections are vast. A well-informed approach to liver health can lead to improved patient outcomes. Recognizing dermatological signs as possible indicators of hepatic dysfunction allows for timely interventions. Through an enhanced understanding of this relationship, healthcare professionals may implement more effective treatment strategies, potentially mitigating more severe health issues down the line.
"Rash symptoms should not be dismissed, but rather viewed as a potential indicator of liver health and overall well-being."
In closing, a comprehensive understanding of the rashes associated with liver disease can optimize both diagnosis and treatment. The continuous exploration of these associations not only aids practitioners but also empowers patients to seek timely medical advice.
Preamble
Liver disease encompasses a wide range of conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s overall health. Among the various manifestations of liver dysfunction, skin rashes have emerged as a particularly important symptom, often serving as a visible indicator of underlying hepatic issues. Understanding the connection between liver disease and rashes not only aids in diagnosis but also enhances awareness of the body's complex interrelationships.
In this article, we will explore the different types of liver disease and their associated rashes. By examining specific conditions such as alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis, and cirrhosis, we will illustrate how these diseases can lead to notable dermatological symptoms. The significance of recognizing these rashes cannot be overstated, as they can assist healthcare professionals in making more informed decisions about patient care.
Careful diagnostic approaches, including physical examinations and laboratory tests, are essential in identifying the nature of liver disease and the ramifications it may have on skin health. As we delve deeper into the characteristics of rashes associated with liver disease, we will discuss management options and the importance of addressing the underlying conditions.
Furthermore, liver functionality plays a pivotal role in maintaining skin health. Understanding how liver dysfunction disrupts this process is crucial for recognizing the etiology behind specific skin manifestations. By employing a comprehensive approach to studying this relationship, we aim to provide valuable insights that will benefit students, researchers, educators, and healthcare professionals alike.
"Skin rashes can serve as critical clues to liver dysfunction, highlighting the need for meticulous examination in clinical practice."
This exploration of the various presentations of rashes linked to liver disease aims to inform and educate about the significance of such symptoms. Whether for clinical application or personal knowledge, gaining a deeper understanding of this topic will foster better recognition of the potential indicators of liver conditions.
Understanding Liver Disease
Liver disease encompasses a variety of conditions that adversely affect the liver's ability to function properly. Understanding liver disease is vital because it highlights the significance of the liver in maintaining overall health and its impact on different systems in the body. The liver plays a critical role in metabolism, detoxification, and producing essential proteins, hence any dysfunction can lead to various health complications.
Recognizing liver disease early can pave the way for timely interventions. This reduces the risk of severe complications such as cirrhosis, liver failure, or even liver cancer. Awareness of liver disease symptoms is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals, particularly as certain manifestations can be subtle. This article aims to underscore the connection between liver disease and dermatological symptoms, enabling a holistic approach to diagnosis and management.
Definition
Liver disease refers to any health disorder that impacts the liver's function. This encompasses a range of conditions, from those that cause inflammation, like hepatitis, to structural progressive illnesses like cirrhosis. With the liver's many roles, even minor conditions can significantly affect bodily functions. Definitions vary slightly based on specific classification, yet they commonly include acute and chronic liver diseases, each with unique challenges.
Common Types of Liver Disease
Understanding the various types of liver diseases is crucial in highlighting their respective characteristics and implications.
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease is primarily caused by excessive alcohol consumption. This condition can lead to inflammation of the liver, fatty liver, and ultimately cirrhosis. Key characteristics include symptoms such as jaundice, ascites, and abdominal pain. It stands out in discussions regarding liver disease due to its preventable nature. People can avoid this condition through lifestyle changes and moderation of alcohol intake. Recognizing its unique feature is significant: it emphasizes the impact of lifestyle choices on liver health.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver, can be viral or non-viral. Viral hepatitis types A, B, C, D, and E differ in transmission methods and severity of illnesses they cause. A key characteristic of hepatitis is its potential for acute or chronic outcomes. This discussion is essential for the article, as hepatitis is a leading cause of liver-related morbidity. Understanding the unique features of each virus can help tailor prevention strategies and therapeutic approaches.


Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis represents the end-stage of liver disease resulting from various chronic liver conditions, including chronic hepatitis and alcoholic liver disease. A significant aspect of cirrhosis is its irreversible nature, often leading to severe liver dysfunction or failure. This characteristic differentiates it from earlier-stage liver diseases which may be more amenable to treatment. Highlighting cirrhosis in this article allows for discussions on the most critical management options, including liver transplantation.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is characterized by abnormal fat accumulation in the liver. It can be divided into alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. A critical aspect of fatty liver disease is its current prevalence, especially in the context of rising obesity rates and metabolic syndrome. The unique feature of this disease is its often asymptomatic nature during early stages. Early recognition and management are essential to prevent progression to severe liver damage.
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Understanding the symptoms of liver disease is critical for early recognition and management of hepatic conditions. Symptoms can indicate liver dysfunction and potential complications. Awareness of these symptoms can lead to timely medical intervention, which is crucial in preventing further liver damage and improving patient outcomes. Among the various symptoms, some are general and indicate underlying systemic issues, while others are more specific and can point directly to liver dysfunction.
General Symptoms
General symptoms often include fatigue, jaundice, itchy skin, and ascites. Recognizing these signs can help in identifying the extent of liver disease and guiding further diagnostic evaluation. Each symptom serves a unique purpose in understanding liver health.
Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common complaints among patients with liver disease. It manifests as a pervasive feeling of tiredness that is not alleviated by rest. This symptom can stem from various causes, including the build-up of toxins due to impaired liver function and metabolic disturbances. Fatigue is particularly significant because it often indicates the overall decline in liver health, prompting further evaluation and possibly aggressive management of the underlying condition. Its consistent presence can signal to both patients and healthcare providers that liver function may be compromised.
Jaundice
Jaundice presents as a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. This occurs when there is an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, a product of red blood cell breakdown that the liver normally processes. Jaundice is a key indicator of liver dysfunction and can alert healthcare professionals to potential liver disease. The unique feature of jaundice is its visible nature, making it a readily noticeable symptom for patients and those around them. The presence of jaundice often leads to more comprehensive liver evaluations and interventions.
Itchy Skin
Itchy skin, or pruritus, can occur in liver disease due to the accumulation of bile salts in the blood. This symptom can be quite bothersome and may worsen at night. The significance of itchy skin lies in its potential to indicate cholestasis, a condition where bile flow is obstructed. For many patients, the discomfort from itchy skin leads them to seek medical help, which could result in an earlier diagnosis of liver disease. Managing this symptom is important not only for comfort but also for addressing the underlying causes.
Ascites
Ascites refers to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, often resulting from liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. This symptom can cause significant discomfort and complicate daily activities. Ascites serves as a marker of advanced liver disease and indicates severe underlying pathological changes. Its presence often necessitates intervention, such as diuretics or paracentesis, highlighting the importance of recognizing ascites as a serious complication that can signal worsening liver function.
Dermatological Symptoms
In addition to these general symptoms, dermatological manifestations can also arise in liver disease. These can include specific rashes and skin changes that are direct effects of liver dysfunction. Recognizing these symptoms is essential, as they may be some of the first indications of liver issues. Medical professionals must consider both internal symptoms and external dermatological signs when assessing liver health.
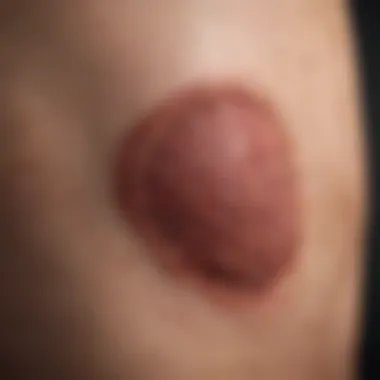
Rash Characteristics in Liver Disease
Understanding the rash characteristics associated with liver disease is crucial. These rashes often serve as visible indicators of underlying hepatic dysfunction. By examining the types, locations, and distributions of rashes, healthcare professionals can better assess the severity of liver conditions. Rashes related to liver disease can signify serious conditions, and recognizing these signs enables early intervention, which is essential for patient management.
Types of Rashes
Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is marked by raised, itchy welts on the skin. This rash arises from the release of histamine, often triggered by allergies or stress. In the context of liver disease, the presence of hives can indicate an allergic reaction or a response to liver toxins. The key characteristic of urticaria is its transient nature; it can appear and disappear quickly, making it a notable symptom in monitoring liver conditions. While urticaria itself is often not serious, its appearance may suggest other underlying health issues that need to be investigated. This makes it a relevant point of interest in the article.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by thick, red patches of skin covered with silvery scales. This rash can be particularly significant in patients with liver disease, as it often indicates systemic inflammation. One key characteristic of psoriasis is that it tends to be persistent and may lead to significant discomfort for the patient. This rash is beneficial to discuss in the article because its chronic nature can complicate the management of liver disease and highlight the need for comprehensive treatment strategies. However, psoriasis can also be managed through various therapies, which can aid in improving the overall quality of life for affected individuals.
Xanthomas
Xanthomas are fatty deposits that appear under the skin, often presenting as yellowish lesions. They are particularly associated with liver disease related to metabolic disturbances, especially those affecting lipid metabolism. The key characteristic of xanthomas is their direct linkage to cholesterol levels and liver function. Their presence serves as an important indicator of dyslipidemia in liver disease, thus making it a critical aspect of the discussion in this article. While xanthomas themselves are not harmful, their appearance can lead to further investigations into a patient’s lipid profiles and overall liver health.
Spider Angiomas
Spider angiomas are small, red, spider-like blood vessels that often appear on the face, neck, and upper body. They can be an indication of hormonal changes often associated with liver dysfunction. The key characteristic of spider angiomas is their distinctive appearance, which can be alarming for patients. Discussing this rash is valuable for this article because it can be both a diagnostic clue for liver disease and a cosmetic concern for patients. While they pose no health risk, their presence can lead to considerable psychological impact, reinforcing the need to address the psychological aspects when managing liver disease.
Location and Distribution
The location and distribution of rashes linked to liver disease provide essential clues for accurate diagnosis. For instance, spider angiomas frequently appear on the chest and upper extremities, while xanthomas may appear near pressure points such as elbows or knees. Hives can appear anywhere on the body but often shift rapidly. Psoriasis may also have a pattern of severity based on the areas affected. By recognizing these patterns, healthcare professionals can perform more targeted investigations and provide more effective management for patients, emphasizing the importance of thorough physical assessments.
Pathophysiology of Rashes in Liver Disease

The pathophysiology of rashes associated with liver disease is a critical aspect that sheds light on how liver health directly influences skin conditions. Understanding the underlying mechanisms helps practitioners identify systemic issues that may manifest as dermatological symptoms. The liver plays a central role in metabolism, detoxification, and synthesis of crucial proteins, all of which are essential for maintaining healthy skin. Consequently, when liver function deteriorates, the resultant imbalances and toxic accumulations can lead to a variety of rashes.
Liver Function in Skin Health
The liver's functions are vital for skin integrity and health. It synthesizes albumin, which helps maintain plasma oncotic pressure and hydration levels. Moreover, it metabolizes hormones, vitamins, and minerals that are essential for skin vitality. The liver also assists in eliminating toxins from the bloodstream. When liver function is optimal, the skin benefits from enhanced circulation and nutrient delivery, leading to a clear and healthy appearance.
Changes in liver function can show through skin manifestations. For example, the accumulation of bilirubin leads to jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and sclera. This can occur in conditions like hepatitis where liver function is severely impaired. In addition, the liver impacts the synthesis of keratinocytes and the skin barrier, disruptions of which result in skin dryness or increased sensitivity. Understanding these connections enables healthcare providers to monitor liver health through dermatological signs, making rashes relevant indicators of hepatic dysfunction.
Impact of Liver Dysfunction
When liver dysfunction occurs, the consequences are not limited to the liver alone; the skin also pays a price. Liver diseases such as cirrhosis or hepatitis alter normal blood flow, result in toxic accumulation, and disrupt hormonal balance. This can lead to various skin issues. For instance:
- Jaundice - This indicates the failure of the liver to process bilirubin.
- Xanthomas - Fat deposits appearing on the skin can occur due to lipid metabolism dysregulation.
- Spider Angiomas - Small, red, spider-like blood vessels can emerge on the skin as a result of altered hormone levels, particularly estrogen.
Moreover, systemic inflammation arising from liver diseases can lead to conditions like urticaria or chronic pruritus. Scratching can exacerbate skin integrity, leading to infections or further complications. Thus, recognizing the interplay between liver health and skin presentation is crucial for timely management and treatment.
Understanding the pathophysiology behind rashes associated with liver disease is fundamental for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans.
In summary, the liver's health directly impacts the skin's condition. Any dysfunction in liver function can lead to various dermatological symptoms. Hence, understanding the pathophysiology of these rashes equips health professionals to address both the skin symptoms and the underlying liver conditions efficiently.
Diagnostic Approaches
The role of diagnostic approaches in understanding rashes associated with liver disease is crucial. Accurate diagnosis can guide effective treatment and management of symptoms, including dermatological manifestations. Recognizing specific signs and testing for underlying liver dysfunction enables healthcare professionals to tailor interventions to individual patients. Early diagnosis improves outcomes and can potentially prevent further complications related to liver disease.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is the first step in diagnosing rashes linked to liver disease. Clinicians will look for visible changes on the skin, such as color alterations, textures, and shapes of the rashes. They assess the distribution pattern as well. These observations can provide preliminary clues to the presence of liver dysfunction. For instance, certain rashes like spider angiomas can be indicative of underlying liver conditions. A well-conducted physical examination also allows health professionals to engage in valuable discussions with patients about their symptoms and general well-being.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests play an essential role in confirming liver dysfunction and correlating it with skin conditions. They provide objective data, helping to establish a clearer link between liver health and dermatological symptoms. Here are key components of this diagnostic strategy:
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests measure various enzymes and proteins in the blood, reflecting the liver's ability to perform its functions. These tests include aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). These enzymes are released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged, hence an elevation indicates potential liver disease.
Their ease of access and interpretative straightforwardness make liver function tests a preferred choice in clinical practice. However, they may not always provide a complete picture, as some liver diseases may not significantly alter these values.
Bilirubin Levels
Measuring bilirubin levels is essential since elevated bilirubin can lead to jaundice, which is often visible on the skin. Bilirubin results from the breakdown of hemoglobin and is processed by the liver. An increase in bilirubin levels points to impairment in liver function or bile secretion.
This test's importance lies in its direct relationship to observable symptoms of liver disease. However, the interpretation can be complex. Conditions affecting bilirubin metabolism might not necessarily indicate liver disease.
Viral Markers
Checking for viral markers is crucial, especially in cases of hepatitis. Tests look for specific antibodies or antigens in the blood, indicating the presence of viruses like Hepatitis B or C. The presence of viral markers can help in diagnosing chronic liver issues and correlating them with skin manifestations.
Viral marker testing is a valuable diagnostic tool since early detection enables timely intervention. However, it may not address all potential causes of liver disease.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are integral for visualizing liver structure and function. These non-invasive methods help in detecting abnormalities that may contribute to cutaneous symptoms. They provide additional information that laboratory tests might not reveal alone.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is often the first imaging test performed. It can identify liver size, texture, and any masses or lesions. The non-invasive nature and lack of radiation make it a popular choice for initial assessments. Though not perfectly definitive, ultrasound helps in ruling out certain conditions quickly, such as fatty liver disease or cirrhosis.
CT Scan
Computed tomography (CT) offers detailed images of liver structures. It provides comprehensive insight into large lesions or tumors and the surrounding organs. While its sensitivity is high, the exposure to radiation is a consideration, especially in repeated tests.
MR Imaging


Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is particularly useful for assessing liver pathology and blood vessels. It offers high-resolution images without ionizing radiation, which is an advantage over CT scans. MRI can be complex and may be more costly, yet its detailed views facilitate accurate diagnostics.
Management of Rashes
The management of rashes associated with liver disease is critical for both patient comfort and the overall understanding of dermatological implications linked to hepatic dysfunction. These rashes are not merely superficial issues; they can indicate deeper, systemic problems that may require extensive treatment strategies. Effective management can enhance the quality of life for those afflicted and may also serve as a window into the underlying liver function, guiding therapeutic interventions.
It is essential to recognize that rashes can vary widely in presentation, necessitating a tailored approach to treatment. This section will delve into both topical and systemic treatment options that address these dermatological manifestations. By targeting the specific types of rashes and understanding their etiology, healthcare professionals can provide more effective care.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against rashes related to liver disease. These products, which include creams, ointments, and lotions, are generally applied directly to the skin where the rash occurs. They can provide localized relief and may help in combating inflammation, itching, and discomfort.
Such treatments may include corticosteroid creams which reduce inflammation in cases of dermatitis or psoriasis. Other options may include moisturizing lotions that assist with dry skin and irritation. The choice of topical treatment often hinges on the rash's specific characteristics and the patient's overall skin condition.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments are employed when topical options are not sufficient to control the rash or when the underlying condition necessitates an internal approach. These can involve the use of medication that affects the body as a whole and can provide relief from symptoms more effectively.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a hallmark therapy for managing inflammatory skin conditions. They work by suppressing the immune response, which can reduce inflammation significantly. This class of medications is often favored due to its rapid action and efficacy in alleviating symptoms.
A key characteristic of corticosteroids is their broad utility across various dermatological issues associated with liver disease. They are particularly beneficial for managing conditions like psoriasis or urticaria, which may arise due to liver dysfunction. However, corticosteroids also carry disadvantages; prolonged use can lead to skin thinning or other systemic effects, such as adrenal suppression. This necessitates careful monitoring by healthcare providers during treatment.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are frequently used to mitigate itching and discomfort accompanying rashes due to liver disease. They block histamine action, which often causes itching; this can bring considerable relief for patients. Their widespread availability makes them a popular choice in the management of skin conditions.
A defining feature of antihistamines is their fast action in controlling symptoms. While they tend to be well tolerated, side effects like drowsiness can limit their use in some individuals. All patients should be informed about these potential effects when considering antihistamine therapy.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy plays a role in more severe or persistent dermatological rashes associated with liver disease. This treatment option modulates the immune response, making it effective against autoimmune skin disorders that may arise due to liver dysfunction.
A notable advantage of immunosuppressive therapy is its ability to address more complex cases that do not respond well to traditional therapies. However, one must tread carefully due to the risk of increased susceptibility to infections, a significant concern in this population especially when liver function is compromised.
Addressing Underlying Liver Disease
The most effective management of rash related to liver disease ultimately requires a focus on the underlying liver condition. Treating the liver disease may lead to a reduction in rash severity or frequency. Modifying lifestyle factors, employing appropriate medications, or even considering surgical interventions can all form part of a holistic approach to care. This strategy ensures that the patient receives comprehensive treatment that factors in both dermatological and hepatological health.
Closure
The topic of rash associated with liver disease is a significant aspect of understanding the broader implications of hepatic dysfunction. Recognizing the dermatological manifestations can aid in the earlier identification of underlying liver conditions. Rashes may not only serve as superficial symptoms but can also indicate deeper systemic issues related to liver health.
Analyzing the connection between skin presentations and liver disease opens pathways for further research and clinical practice. For healthcare professionals, understanding these manifestations can help guide diagnostic and treatment strategies, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Some key points to consider include:
- Importance of Early Detection: Rashes can be indicative of liver conditions like cirrhosis or hepatitis. Early recognition can lead to timely intervention.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Evaluating rashes should be done in conjunction with other diagnostic methods, including laboratory tests and imaging studies. This holistic approach reinforces the importance of a comprehensive assessment in patient care.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about potential skin symptoms can empower them to seek medical advice sooner, thus fostering a proactive approach to their health.
Rashes linked to liver disease should not be dismissed as mere cosmetic issues; they are often harbingers of significant health challenges.
Overall, the conclusion underscores the necessity for continued education and research into the relationship between liver health and dermatological symptoms. Such knowledge not only enhances clinical practices but ultimately benefits patient care significantly.
Importance of References
- Validity of Information: The references allow readers to verify the authenticity of the information. They provide a pathway to the original research, clinical guidelines, and expert opinions that forms the foundation of the findings discussed. This is especially relevant when addressing complex and nuanced topics like liver disease and its manifestations on the skin.
- Enhanced Understanding: By providing references, the writer signals to the reader that there exists a broader body of work on the effect of liver health on skin conditions. This may include studies that explore various aspects, such as:
- Guiding Further Research: For students, researchers, and healthcare professionals, references serve as a gateway to further exploration. They often indicate pivotal research trajectories or landmark studies that have shaped the current understanding of liver-related rashes.
- The biochemical pathways involved in liver function.
- Case studies demonstrating specific rashes associated with liver diseases.
- Insights from dermatology and hepatology that highlight interconnectivity between the two fields.
Benefits and Considerations
Providing references enhances the article's academic rigor. It reassures the audience of the reliability of the content. For instance, referencing peer-reviewed journals, reputable medical websites, or authoritative textbooks establishes a foundation upon which readers can rely.
"A well-referenced article is an invaluable tool for readers seeking to deepen their understanding of a topic."
However, careful consideration must also be given to the selection of sources. Not all articles are equal; the scope of research, the reputation of the journals, and the authors' qualifications must all be taken into account. This discernment ensures that the information presented is not only accurate but also applicable to current clinical practice.
Listing references appropriate to the content discussed throughout the article is essential. The inclusion should follow a consistent format, making it easy for readers to locate these resources.



