Hawksbill Turtle Conservation: Current Status and Efforts

Intro
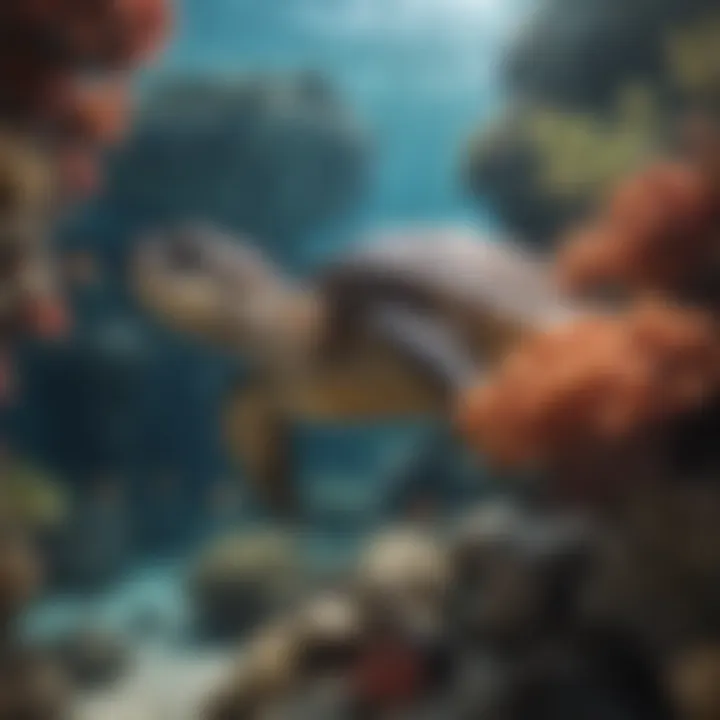
The Hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) holds a unique position in marine ecosystems. Its existence is pivotal for maintaining the health of coral reefs, which are critical to biodiversity. However, the species is classified as critically endangered. This status arises from several factors, primarily linked to human activities. The aim of this article is to meticulously unveil the conservation status of the Hawksbill turtle while addressing the myriad of threats it faces and exploring existing conservation efforts.
Methodologies
Description of Research Techniques
Research into the conservation status of the Hawksbill turtle primarily employs a mix of field studies and remote sensing. Field studies often involve tagging and monitoring turtles to gather data on their movement patterns. Researchers utilize various observational methods to assess population size and health.
Remote sensing technology plays a role in understanding habitat quality and distribution. Satellite imagery is frequently used to monitor changes in marine environments, especially around nesting beaches. This dual approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of both the turtles and their habitats.
Tools and Technologies Used
Different tools enhance the research process. GPS tracking devices are commonly deployed to monitor movements over large distances. Genetic sampling techniques help in understanding population structure and diversity.
Furthermore, software like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) aids in analyzing spatial data related to turtle habitats and human activities. The integration of these tools fosters a clearer picture of conservation needs.
Discussion
Comparison with Previous Research
Historically, the status of Hawksbill turtles has been closely examined. Early studies focused primarily on direct threats like poaching and habitat loss. Recent research, however, highlights the compounded effects of climate change and pollution, which previous studies may have underestimated. The increase in ocean temperatures affects nesting sites and hatchling survival rates, making recent research crucial.
Theoretical Implications
The findings suggest a need for updated conservation models. Current theoretical frameworks must adapt to include the increasing uncertainties posed by climate change. Addressing these implications requires a multi-faceted approach, engaging international stakeholders to work collaboratively toward effective conservation strategies.
Effective conservation of Hawksbill turtles demands an integrated approach that combines local efforts with global policies.
Overall, understanding the current conservation status of Hawksbill turtles is critical. It reveals not only the species' plight but also underscores the need for ongoing research and collaboration in the field of marine conservation.
Intro to Hawksbill Turtles
The Hawksbill turtle is an essential subject in the realm of marine conservation. Understanding its status helps in grasping the complexities involved in protecting not just this species, but broader marine ecosystems. Hawksbill turtles play a vital role in marine environments, particularly in maintaining the health of coral reefs. Their foraging habits impact coral reef dynamics by controlling sponge populations.
Species Overview
Hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) are strikingly beautiful, with a uniquely patterned shell that varies in hues of amber, brown, and yellow. These turtles usually measure between 26 to 33 inches in carapace length and can weigh from 100 to 150 pounds. They are distinguished by their narrow heads and long, pointed beaks, which help them to feed on sponges and other invertebrates found in coral reefs. The diet is critical as it influences reef health, particularly due to their role in keeping sponge populations in check.
Hawksbill turtles are known for their migratory behavior. They travel long distances between feeding and nesting sites. This trait is significant for their survival and ecological contribution but makes them vulnerable to human impacts like habitat destruction and climate change. Understanding their biology and behavior is crucial for effective conservation strategies.
Historical Distribution
Historically, Hawksbill turtles enjoyed a wide distribution across tropical and subtropical oceans. They were once abundant in the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Indian Ocean. Nesting sites were primarily found on sandy beaches, predominantly in the Caribbean and parts of the Pacific Ocean.
However, various anthropogenic pressures have led to a drastic decline in their populations and nesting habitats. Factors such as overharvesting for their shells, loss of nesting beaches due to coastal development, and pollution greatly reduced their numbers. In recent decades, efforts have been made to protect their habitats, yet their historical ranges continue to be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
Understanding the historical distribution of Hawksbill turtles informs contemporary conservation efforts, allowing stakeholders to restore and protect critical habitats.
Current Conservation Status
Understanding the current conservation status of the Hawksbill turtle is essential to addressing the threats it faces. This section looks at the IUCN Red List assessment and population estimates, providing a detailed overview of the species' their ecological significance, and insights into ongoing conservation efforts.
IUCN Red List Assessment
The IUCN Red List is a critical tool used to assess the conservation status of species globally. For Hawksbill turtles, as of now, they are classified as Critically Endangered. This classification underscores the urgency of conservation action. Several factors contribute to this status, including habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
"The critically endangered status of the Hawksbill turtle serves as a stark reminder of the fragile balance within marine ecosystems."
In the past, Hawksbill populations were more abundant, but overfishing and illegal trade of their shells have dramatically reduced their numbers. Moreover, habitat degradation through coastal development and pollution only compounds these challenges. Efforts to monitor and assess their populations are ongoing, but the impact of human activities continues to hinder recovery.
Population Estimates


Obtaining reliable population estimates for Hawksbill turtles is fraught with difficulties, mainly due to their migratory nature and the vast ocean areas they inhabit. Current estimates suggest that the population numbers are scattered and may range between 15,000 and 25,000 nesting females worldwide.
Population numbers vary significantly, with certain regions experiencing steeper declines than others. For example, in the Caribbean and certain parts of the Indo-Pacific, population assessments reveal troubling trends, indicating that local populations may be less than sustainable.
The need for further research is paramount. Effective population monitoring helps direct conservation efforts where they are needed most. The integration of modern technologies like satellite tracking and genetic studies could enhance our understanding of Hawksbill turtle populations, influencing policy and conservation strategies moving forward.
Overall, addressing the current conservation status of Hawksbill turtles is pivotal. It lays the groundwork for informed actions and global collaboration necessary for the survival of this species.
Ecological Importance
The ecological significance of Hawksbill turtles goes far beyond their charming appearance. These creatures play critical roles in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. Their presence indicates the overall health of the ocean, signifying a well-balanced environment.
Role in Marine Ecosystems
Hawksbill turtles are primarily benthic feeders. They consume a variety of invertebrates, with a particular preference for sponges. This feeding behavior aids in controlling sponge populations that could otherwise overpopulate and harm coral reefs. By regulating sponge growth, Hawksbill turtles enhance the availability of space for coral recruitment and growth. The impact of their diet on ecosystem dynamics elevates their role in promoting biodiversity.
Moreover, when Hawksbill turtles graze on sponges and other invertebrates, they contribute to the balance of marine food webs. Many species rely on healthy coral reefs, and the happy interactions among species foster resilience against environmental changes. By assisting in these processes, Hawksbill turtles exemplify the crucial interconnectedness of marine life.
Impact on Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are often described as underwater cities, bustling with life. The presence of Hawksbill turtles is integral to their maintenance. They contribute to coral health indirectly by controlling the populations of organisms that might otherwise harm these reefs. As Hawksbill turtles thrive, they promote the overall diversity of marine life.
Additionally, their activities enhance the structural integrity of the reefs. Healthy coral reefs serve as habitat for countless marine species, significantly impacting fish populations and other marine life. This interaction fortifies the ecosystem's stability.
"Hawksbill turtles play a critical role in maintaining the balance of coral reefs, which are essential for the health of marine biodiversity."
As this relationship demonstrates, the conservation of Hawksbill turtles is not merely an act of protecting a single species. It is, in essence, a commitment to preserving the intricate web of life that relies on the stability of coral reefs and the broader marine ecosystems. Their decline sends ripples through these ecosystems, emphasizing the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Threats to Hawksbill Turtles
Understanding the threats to Hawksbill turtles is crucial for highlighting the pressing challenges these creatures face. As a critically endangered species, Hawksbill turtles encounter a multitude of dangers that significantly affect their populations and habitats. Recognizing these threats sets the stage for effective conservation strategies and is central to this discussion. This section will delineate three primary threats: habitat loss, illegal trade, and the impacts of climate change. Each of these elements plays a vital role in the survival of the species, and addressing them is essential for their future.
Habitat Loss
Habitat loss poses one of the most significant threats to Hawksbill turtles. Their nesting beaches and foraging grounds are often compromised by coastal developments, pollution, and human encroachment. The destruction of coral reefs and mangroves has direct implications on their feeding and breeding habits. Coral reef degradation specifically impacts Hawksbill diets, as they primarily feed on sponges found in these ecosystems.
To illustrate, development projects might clear coastal areas for tourism or urban sprawl, leading to a decrease in suitable nesting locations. Additionally, the increasing use of plastic products contributes to habitat deterioration. Turtles often ingest plastic debris, mistaking it for food, which subsequently affects their health and reproduction.
Illegal Trade
Illegal trade of Hawksbill turtles remains a critical concern. Their shells are highly sought after for ornamental purposes, leading to poaching and trafficking. Despite protections under international laws such as CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species), enforcement remains a significant challenge.
Hawksbill turtles, due to their striking shells, often fall victim to targeted illegal fishing. This criminal activity not only threatens individual turtles but also disrupts the broader ecological balance. The existence of a black market for turtle shells signals a troubling disregard for conservation efforts. Much of the illegal trade occurs online, complicating regulatory frameworks and making it increasingly difficult to track activities effectively.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change is another formidable threat to Hawksbill turtles. Rising ocean temperatures and acidification affect coral reefs, their primary habitat. As water becomes warmer, coral bleaching events increase, compromising the turtles’ feeding grounds.
Moreover, rising sea levels are leading to the loss of nesting beaches, which may become submerged or eroded. Increased storm intensity can also wash away nests before they have a chance to hatch, significantly impacting population numbers. Behavior patterns of Hawksbill turtles, including nesting times and locations, are also altered by changing environmental conditions. Adaptability may not keep pace with these rapid changes, threatening their survival in the long term.
In summary, these threats interplay and exacerbate each other, producing a dire situation for Hawksbill turtles. Recognizing the scale of habitat loss, illegal trade, and climate change effects is essential for implementing well-informed conservation strategies. To adequately protect Hawksbill turtles, collaborative efforts and robust policy-making must address each of these challenges collectively.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for Hawksbill turtles are paramount in ensuring the survival of this critically endangered species. These initiatives are organized at various levels and involve different stakeholders, including governments, non-governmental organizations, local communities, and international bodies. The need for effective conservation strategies is underscored by the severe threats that Hawksbill turtles face, which necessitate comprehensive actions across multiple fronts.
International Treaties and Agreements
International treaties play a crucial role in the protection of Hawksbill turtles. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) is one of the most significant agreements. CITES lists Hawksbill turtles under Appendix I, prohibiting international trade except under exceptional circumstances. This legal framework helps to mitigate the illegal trade in their shells, which has historically contributed to their decline.
In addition, the United Nations Environment Programme's Convention on Biological Diversity supports the conservation of Hawksbills through various programs aimed at marine biodiversity. Countries that are party to this agreement commit to protecting and managing their marine resources, addressing threats that impact Hawksbill habitats and populations.
"Global collaboration through treaties helps create a united front against the challenges faced by Hawksbill turtles."


Local and Global Initiatives
Conservation efforts also manifest through local and global initiatives aimed at protecting Hawksbill turtles. Many non-profit organizations, such as The Sea Turtle Conservancy and Oceanic Preservation Society, run programs focused on habitat restoration, community engagement, and direct protection measures for nesting sites.
Local communities often take the lead in these efforts. For instance, in areas where Hawksbills nest, community-led programs raise awareness and encourage the protection of nesting beaches. Engaging residents not only fosters stewardship of local ecosystems but also provides economic alternatives to activities that threaten turtle populations, like illegal fishing or poaching.
On a global scale, collaborative research projects gather data on Hawksbill populations and behavior, enabling more effective conservation strategies. This data not only informs policymakers but also helps in tailoring on-the-ground initiatives that resonate with local contexts.
In summary, the multifaceted approach to Hawksbill turtle conservation—through international treaties and local initiatives—is essential for positioning this species toward recovery. The intersection of law, community involvement, and scientific research creates a comprehensive framework for conservation that acknowledges the complex challenges these turtles face.
Research and Monitoring
Research and monitoring play a crucial role in the conservation status of Hawksbill turtles. Through systematic studies, conservationists can gather data on the population dynamics, biology, and behavior of these turtles. This information is vital in developing effective conservation strategies. Moreover, ongoing monitoring efforts enable researchers to assess the success of these strategies and make necessary adjustments.
The importance of research goes beyond understanding species alone; it involves investigating the impact of environmental changes and human activity on Hawksbill turtle populations. This multidimensional approach helps identify the most pressing threats and informs targeted interventions. Collaborative efforts between scientists, governments, and local communities enhance the effectiveness of conservation programs.
Current Research Projects
Current research projects on Hawksbill turtles focus on various aspects of their lives. These studies often include:
- Habitat utilization: Understanding the specific areas that Hawksbill turtles frequent is important for effective habitat protection.
- Migration patterns: Tracking the migratory paths helps identify critical feeding and nesting sites, crucial for species survival.
- Genetic studies: Researching genetic diversity can provide insight into the health of turtle populations and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
Some notable projects include studies in the Caribbean and the Pacific, where researchers are installing satellite tracking devices on turtles. This technology captures real-time data about their movements and behaviors. These findings contribute valuable insights into their migratory routes and habitat preferences, helping guide conservationists in creating protective measures.
Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods for Hawksbill turtles vary widely, incorporating both traditional and innovative techniques.
- Visual Surveys: Researchers often conduct visual surveys during nesting seasons to estimate population numbers and nesting success rates.
- Satellite Tracking: This method involves attaching GPS devices to turtles. The data collected helps researchers understand migration habits and environmental interactions.
- Environmental DNA (eDNA) Sampling: This newer method involves collecting water samples to detect the presence of turtle DNA. This can be particularly useful in areas difficult to access.
- Photo Identification: Individual turtles often have unique shell patterns. This technique allows for tracking of specific turtles over time, providing insight into individual health and behavior.
"Monitoring efforts provide the ongoing feedback necessary to adaptively manage conservation interventions for Hawksbill turtles."
These methods contribute to a comprehensive understanding of Hawksbill turtle populations. By combining data from different sources, researchers can create a more accurate picture of the conservation status of this critically endangered species. The resulting knowledge forms the basis for effective policies and conservation strategies.
Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement and education are pivotal elements in the conservation of Hawksbill turtles. Involving local communities is crucial because these populations often interact directly with marine environments. Their involvement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards conservation practices. When communities understand the ecological and economic value of Hawksbill turtles, they are more likely to engage in protective behaviors and support conservation initiatives.
Educating communities about the significance of Hawksbill turtles can also lead to more protective measures for their habitats. Knowledge sharing helps reduce misinformation surrounding turtle biology and conservation needs. Moreover, it empowers communities to participate in conservation activities, aligning local interests with global conservation goals.
Role of Local Communities
Local communities play an essential role in Hawksbill turtle conservation. The actions they take can greatly influence the health of local ecosystems. For instance, communities can help protect nesting sites from poaching or development. Engaging local fishers in sustainable practices can lead to reduced bycatch and habitat destruction.
In many areas, initiatives have successfully mobilized communities to monitor nesting beaches, report illegal activities, and participate in clean-up efforts. These actions not only directly contribute to the conservation of Hawksbill turtles but also foster community pride and cohesion.
Outreach programs that include local participation can also enhance the success of conservation efforts. Tailoring strategies that consider cultural, social, and economic contexts can lead to more effective programs. This approach can yield benefits such as:
- Enhanced ecological knowledge
- Improved livelihoods through sustainable practices
- Strengthened community resilience against environmental threats
Educational Campaigns
Educational campaigns are vital for raising awareness about the plight of Hawksbill turtles. These campaigns can provide essential information about the species and the various threats they face. Informative materials, such as pamphlets, workshops, and online resources, can effectively educate a broader audience.
Effective campaigns often include:
- Workshops and Seminars: Conducting interactive sessions can engage different age groups, allowing for deeper learning and participation.
- Social Media Outreach: Platforms like Facebook and Reddit can be useful tools to share real-time information and updates about conservation efforts.
- School Programs: Integrating conservation topics into school curricula ensures younger generations understand the importance of protecting marine life.
- Collaborative Projects: Partnering with local organizations can amplify outreach and provide various perspectives on conservation issues.
"Through education, we can inspire action. Understanding leads to conservation."
These educational initiatives are not only about conservation; they can also stimulate local economies by promoting eco-tourism and sustainable practices. Overall, community engagement and education form the backbone of effective conservation strategies and have a lasting impact on the protection of Hawksbill turtles.
Case Studies


Understanding the conservation status of Hawksbill turtles requires us to explore real-life examples of both successes and failures. Case studies are vital for illustrating practical applications of conservation techniques and for revealing lessons learned over time. Analyzing these specific instances provides valuable insights into what strategies are effective and which ones may not yield the desired results.
- Significance of Case Studies
Case studies help bridge theory and practice. By examining past initiatives, researchers and conservationists can better inform current methodologies. These cases highlight the nuances of local ecosystems and the diverse challenges that arise. - Benefits of Analyzing Various Cases
- Considerations for Effective Case Studies
- Encourages data-driven decisions.
- Identifies strategies that may be adapted in different contexts.
- Fosters collaboration among conservation groups by sharing best practices.
- Inclusivity of local community perspectives.
- Longitudinal studies to observe long-term impacts.
- Sustainability of methods used in successful initiatives.
Through these lenses, we can uncover vital information that informs future conservation efforts.
Successful Conservation Initiatives
Several successful conservation initiatives exist that focus on Hawksbill turtles, showcasing effective strategies. One prominent example is the Hawksbill Turtle Conservation Project in the Caribbean. This initiative involves local fishermen and non-profit organizations that work together to monitor nesting sites, collect data about turtle populations, and raise awareness in nearby communities.
Initiatives include:
- Nest Monitoring: Community volunteers are trained to monitor and protect nesting habitats.
- Education Programs: Workshops are held in schools to educate young people about the importance of Hawksbill turtles and marine biodiversity.
- Collaborative Research: Various organizations partner with local universities to conduct research on turtle behavior and population dynamics.
The active involvement of local communities in conservation efforts greatly enhances the effectiveness of such initiatives.
Lessons Learned from Conservation Failures
Despite many successful approaches, several conservation efforts for Hawksbill turtles have not reached their intended goals. One notable failure involved the economics of illegal trade, particularly in Southeast Asia. Attempts to protect these turtles through strict enforcement often faced pushback from economic needs of local fishermen relying on turtle products.
Key lessons from these scenarios include:
- Engagement is Crucial: Without the buy-in from local communities, conservation efforts often lack sustainability.
- Need for Economic Alternatives: Providing alternative livelihoods can reduce dependence on illegal trade.
- Importance of Education: Continued educational outreach is essential to foster cultural shifts away from traditional practices that harm turtle populations.
Future Directions
The future of Hawksbill turtle conservation looks to be a landscape shaped by innovative approaches and comprehensive policy frameworks. Significant advancements can emerge from understanding the current challenges and strategically addressing them. Focusing on future directions is crucial because it ensures that efforts are not only reactive but proactive. As situations evolve, so must the strategies to ensure the survival of these critically endangered species.
Policy Recommendations
To effectively safeguard Hawksbill turtles, it is essential to implement robust policy recommendations. These policies must prioritize the integration of conservation efforts into national and local governance. Promoting legislative measures that protect critical habitats is one avenue. This might include:
- Designating marine protected areas that encompass vital nesting and feeding grounds.
- Enhancing legal frameworks to combat illegal trade in turtle shells and products.
- Establishing strict penalties for violations related to Hawksbill turtle poaching and habitat destruction.
Furthermore, involving local communities in policy-making can result in more effective conservation outcomes. Community-based initiatives must encourage sustainable tourism and showcase the economic benefits of preserving Hawksbill turtles. Encouraging stakeholder participation fosters a sense of ownership, thereby increasing public commitment to conservation efforts.
Innovative Conservation Technologies
The adoption of innovative conservation technologies presents a promising avenue for enhancing the effectiveness of Hawksbill turtle conservation. Technological advancements can aid in monitoring populations, protecting habitats, and combatting illegal activities. Some noteworthy technologies include:
- Satellite tracking: This tool allows researchers to monitor the migratory patterns and habitat usage of Hawksbill turtles. By understanding movement behaviors, conservation strategies can be tailored to protect crucial areas.
- Drone surveillance: Drones can survey expansive marine and coastal habitats. This capability is particularly useful for monitoring illegal fishing and poaching activities in hard-to-access areas, providing authorities with real-time data.
- Environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis: By analyzing water samples, researchers can detect the presence of Hawksbill turtles in various habitats. This non-invasive methods allows conservationists to assess population size and distribution without disturbing the animals.
"Innovative technology can revolutionize the way we understand and protect marine biodiversity, including iconic species like the Hawksbill turtle."
Embracing such technologies not only enhances data collection but also enables a more sophisticated approach to monitoring and enforcement. Integration of these tools into existing conservation frameworks can significantly improve the prospects for the future of Hawksbill turtles.
Finale
Concluding this article, it is essential to emphasize the multifaceted importance of understanding the conservation status of Hawksbill turtles. These turtles, now classified as critically endangered, serve as a vital part of marine ecosystems. The sections preceding this conclusion highlighted not only their ecological roles but also the significant threats posed by human activities such as habitat loss, illegal trade, and climate change. Thus, the need for urgent conservation strategies becomes evident.
Summary of Findings
To summarize the findings, Hawksbill turtles play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of marine environments, especially coral reefs. Unfortunately, their populations have drastically declined over the decades due to various threats. Conservation efforts have made some progress, yet challenges remain. Key points include:
- Critical Endangerment: Hawksbill turtles are at serious risk of extinction.
- Human Impact: Activities like poaching and habitat destruction greatly threaten their survival.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative global efforts are essential for their protection.
The gathering of information from various research projects shows that while some local initiatives yield positive results, a more holistic approach is needed.
Call to Action for Conservationists
For conservationists, the call to action is clear. Mobilizing communities and raising awareness about the plight of Hawksbill turtles is imperative. Specific actions might include:
- Engaging Local Stakeholders: Involve local communities in conservation efforts, ensuring they understand the importance of protecting these turtles.
- Policy Advocacy: Work on policies that enact stricter penalties for illegal trade and habitat destruction.
- Education Campaigns: Launch educational initiatives to inform the public, especially in regions where Hawksbill turtles nest.
"Without concerted efforts, the future of Hawksbill turtles is uncertain. Each individual can play a role in their conservation through awareness and activism."



