Best Workouts for Asthma: A Comprehensive Guide


Intro
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Individuals with asthma often struggle with maintaining a regular exercise routine due to concerns over exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. This guide is aimed at shedding light on effective workout strategies for asthma management.
Regular physical activity can be beneficial not only for overall health but also for asthma symptom management. Engaging in the right types of exercise can strengthen the lungs, improve endurance, and enhance quality of life. Understanding the physiological responses to exercise, especially in those with asthma, plays a crucial role in tailoring effective workouts.
This article will delve into specific types of exercises that can be advantageous, strategies to mitigate asthma symptoms during workouts, and essential conditioning techniques. Along with this, we will discuss safety considerations and provide valuable insights for individuals determined to pursue a healthier lifestyle.
By the end of this guide, you should feel empowered to approach physical activities while recognizing and mitigating asthma-related risks effectively.
Understanding Asthma
Understanding asthma is crucial for anyone who wishes to manage their condition effectively while engaging in physical exercise. Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder, which can significantly impact a person's ability to perform daily activities, including workouts. By comprehending the basics of asthma, including its definition, types, and triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to create a safe and effective exercise regimen. This section aims to provide a detailed overview that forms the foundation for better asthma management through exercise, ensuring that individuals understand their own health needs and limitations.
Definition and Types of Asthma
Asthma is characterized by inflammation of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing. Symptoms can include wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. There are several types of asthma, which can include:
- Allergic Asthma: Triggered by allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or mold.
- Non-Allergic Asthma: May be provoked by irritants like smoke or respiratory infections.
- Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: Symptoms may occur during or after exercise, especially in cold or dry conditions.
- Occupational Asthma: Results from exposure to substances in the workplace.
Recognizing these types enables individuals to pinpoint potential triggers and adapt their exercise routines accordingly.
How Asthma Affects Physical Activity
Asthma can pose challenges during physical activity, but understanding these effects is essential. When exertion increases, the demand for oxygen rises, which can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. Factors that can exacerbate asthma during exercise include:
- Environmental Conditions: Cold air can tighten the airways.
- Intensity of Activity: High-intensity workouts may provoke more symptoms than moderate exercises.
Despite these challenges, it is important to note that with the right precautions, physical activity can be beneficial. Regular exercise can improve lung function and overall quality of life for asthma sufferers.
Common Triggers for Asthma Symptoms
Identifying triggers is critical for asthma management, especially when planning workouts. Common triggers include:
- Airborne Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, or animal fur.
- Weather Changes: Cold air or high humidity can impact breathing.
- Exercise: As mentioned, vigorous activity can sometimes lead to asthma symptoms.
- Irritants: Such as smoke, strong odors, or pollution.
By being aware of these triggers, individuals can make informed choices about when and where to exercise, helping to minimize the occurrence of symptoms.
"Understanding asthma and its impact on physical activity is essential for effectively managing the condition and engaging safely in workouts."
In summary, a solid comprehension of asthma, its types, effects on physical activity, and common triggers facilitates better control of one's health. This foundational knowledge allows for safer and more effective exercise, which is further explored in the subsequent sections of the guide.
The Benefits of Exercise for Asthma Management
Engaging in regular exercise has significant implications for asthma management. Understanding these benefits is essential for both individuals with asthma and their support systems. The advantages extend beyond just physical health, influencing emotional wellbeing and overall life satisfaction.
Improved Lung Function
One of the primary benefits of exercising for individuals with asthma is improved lung function. Regular workouts enhance respiratory strength and efficiency. As people with asthma engage in safe, targeted physical activities, their lungs adapt better to the exertion.
Exercise can promote better breathing patterns. Over time, this can lead to increased lung capacity. Additionally, studies show that cardiovascular exercises, such as walking or swimming, can improve overall airflow and reduce airway sensitivity. This capacity for more effective breathing may lead to fewer asthma symptoms in rest periods and when exposed to triggers.
While engaging in aerobic exercises, individuals may find their body able to utilize oxygen more efficiently. This natural adaptation to physical stress may even help in reducing the severity and frequency of asthma attacks.
Enhanced Quality of Life
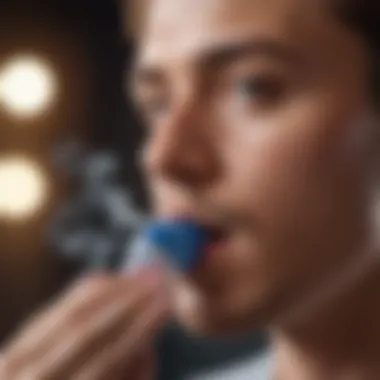

Physical activity can profoundly affect the quality of life for asthma sufferers. Exercise can help alleviate symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue, which often accompany asthma. Regular workouts contribute to increased stamina and endurance, allowing individuals to participate more actively in daily life.
Moreover, exercise has mental health benefits. Many asthma patients experience stress and anxiety related to their condition. Physical activity releases endorphins, naturally elevating mood and enhancing feelings of wellbeing. Thus, by integrating fitness regimes into their routines, many may find significant improvement in how they perceive their health and emotional state.
Weight Management and Overall Health
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for asthma management, as obesity can exacerbate respiratory issues. Regular exercise plays a critical role in controlling weight. It promotes calorie burning, which can help in weight loss and weight maintenance efforts.
Individuals with asthma who exercise consistently often notice other health benefits, including improved heart function and reduced risk of chronic conditions. This can create a positive feedback loop; as fitness levels rise, asthma symptoms may decrease. It is essential to select the right types of workouts to ensure safety while maximizing these health benefits.
In summary, the benefits of exercise extend to lung function, quality of life, and weight management. Individuals with asthma can significantly enhance their physical and mental well-being by engaging in suitable exercises.
Types of Workouts Suitable for Asthma Patients
Understanding the types of workouts appropriate for asthma patients is essential. Exercise's benefits can be significant but require careful selection of activities. The right workouts can enhance lung capacity, improve overall fitness, and reduce asthma symptoms. Low-impact exercises help minimize the risk of triggering asthma attacks. Some suitable options include low-impact aerobic exercises, strength training techniques, and flexibility and stretching practices. Each category holds unique advantages that align with asthma management strategies.
Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises
Low-impact aerobic exercises are crucial for asthma patients. These activities provide cardiovascular benefits while reducing the risks of exacerbating breathing issues. They promote endurance without overexerting the lungs, making them safer choices. Below are specific exercises within this category.
Swimming
Swimming is a recommended workout for asthma patients. The environment of water provides humidity, which can help ease breathing. The aquatic setting reduces the stress on the lungs by maintaining a stable temperature. Thus, swimming becomes a beneficial exercise. It allows for varied intensity and promotes overall fitness without extreme exertion. However, some may experience chlorine sensitivity, which could trigger symptoms in specific pools.
Cycling
Cycling is another suitable choice for asthma sufferers. It allows individuals to control their intensity and pace. This form of exercise can be performed indoors or outdoors, which provides flexibility. Cycling strengthens the cardiovascular system without harsh impacts. Factors like cold air during winter rides can prompt symptoms, making it essential to choose conditions wisely.
Walking
Walking is an accessible and practical option for many. It is low-impact and can be adjusted to individual comfort. Regular walking can significantly benefit lung function over time. Being outdoors provides fresh air and can improve overall mood. However, it is necessary to be aware of environmental triggers, like pollen during certain seasons, which could irritate asthma.
Strength Training Techniques
Strength training is a vital component for overall health benefits for asthma patients. This type of exercise enhances muscular strength while being adaptable. Patients can work to their limits without the high aerobic demand that can strain the lungs. The following techniques offer effective strength training options.
Bodyweight Exercises
Bodyweight exercises are valuable for asthma patients as they require no equipment. This method includes movements like push-ups, squats, and planks. These exercises help build strength gradually and can be modified for any fitness level. The advantage lies in their adaptability and minimal risk for lung strain.
Resistance Bands
Resistance bands provide versatile training without heavy weights. They allow for a controlled intensity, making it easy to manage workouts. The bands facilitate various exercises that target different muscle groups. Importantly, they can be used almost anywhere, offering convenience. However, maintaining proper form is critical to avoid injuries.
Weight Machines
Weight machines can also play a role in strength training for asthma patients. These machines assist in maintaining form and can help limit the risk of injury when used correctly. They usually provide control and support during workouts. However, the intensity should be approached cautiously to ensure it does not trigger symptoms. It is advisable to start with lower weights and gradually increase as strength improves.
Flexibility and Stretching Practices
Flexibility exercises are important for maintaining a range of motion and preventing injury. They can also promote relaxation and help ease tension, beneficial for breathing. Two common practices in this category are yoga and Pilates.
Yoga
Yoga can improve flexibility and promote relaxation. Slow and controlled movements emphasize deep breathing. This approach can enhance lung function and mindfulness. Yoga sessions are often held in a calm environment, which can further reduce stress triggers. However, patients should be cautious of highly vigorous types which may not be suitable.


Pilates
Pilates integrates strength, flexibility, and breathing techniques. Focused on core strength, it combines controlled movements with mindful breathing. This can aid in improving overall fitness without overexertion. Participants need to be mindful, as some poses may need adjustments to suit individual capabilities and comfort levels.
Exercise Considerations for Asthma Sufferers
Engaging in exercise can be an avenue for those with asthma to enhance their lung function and overall well-being, but caution is necessary. Understanding specific considerations helps mitigate risks and maximizes benefits. These factors include consulting healthcare professionals, recognizing personal limitations, and being mindful of timing and environmental influences.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before starting any exercise regimen, individuals with asthma should consult their healthcare providers. This professional input is crucial to tailoring a workout plan that accommodates their unique health profile. Healthcare providers can assess the severity of asthma, recommend appropriate physical activities, and offer strategies to manage asthma symptoms during exercise. They may also advise on the necessity of carrying rescue inhalers or other medications during workouts. This preventative measure is vital, as it prepares individuals for potential symptoms that might arise during exertion.
Understanding Personal Limitations
Awareness of one's own body is essential. Asthma can vary significantly from person to person, impacting endurance and capacity for physical activity. Recognizing when to push forward and when to take a step back can make a significant difference. Take note of how your body feels during and after various exercises. Individuals should avoid high-intensity activities if they lead to discomfort, shortness of breath, or other asthma flare-ups. This self-awareness fosters a balanced approach to exercise.
Timing and Environment Factors
Best Times to Exercise
Timing plays an integral role in asthma management during physical activity. Morning or late evening workouts can often be preferable, as pollen levels and outdoor air pollution tend to be lower during these times. Exercising indoors during peak pollen seasons can also be advantageous. This timing characteristic helps mitigate the likelihood of encountering triggers that can exacerbate symptoms.
Weather Conditions
Weather significantly impacts asthma symptoms. Cold air can induce bronchoconstriction in many individuals. Therefore, exercising in warmer temperatures is recommended when feasible. Humidity levels also influence breathing; extreme humidity can lead to heightened discomfort. Monitoring weather conditions prior to exercising allows individuals to make informed decisions about outdoor activities, enhancing their safety and enjoyment.
Effective Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
Effective warm-up and cool-down routines are paramount for individuals with asthma. These routines prepare the body for exercise, significantly reducing the risk of triggering an asthma attack. Properly executed, these routines can enhance performance, improve flexibility, and ensure a safer exercise experience.
Importance of Warm-Up Exercises
Warm-up exercises serve several important functions. First, they gradually increase the body's core temperature, promoting blood flow to the muscles. This is especially crucial for asthma patients, as it can lessen the risk of bronchospasm. A gradual increase in activity allows the respiratory system to adjust to upcoming physical demands.
Engaging in a regular warm-up routine can also help enhance lung capacity. With specific warm-up activities tailored for asthma, individuals can practice controlled breathing, which aids in preparing the lungs for more vigorous activity. Experts recommend starting with gentle movements. Examples include light jogging or specific stretching exercises. The goal is to progress slowly over a period of 5 to 10 minutes to build up to the intended workout.
Recommended Cool-Down Techniques
Cool-down techniques are just as significant as warm-up exercises. After engaging in physical activities, gradually transitioning to a resting state helps the body restore its normal functions. It is vital for reducing the post-exercise risk of asthma symptoms.
Cool-down routines can involve low-intensity exercises such as walking or slow cycling. These activities can help lower the heart rate smoothly, bringing it back to resting levels. Stretching is also a crucial component of the cool-down phase. It improves flexibility and aids in muscle recovery, which can be beneficial in managing muscle tension that sometimes accompanies asthma.
To optimize overall wellness, it is essential to include both warm-up and cool-down phases into your exercise regimen. They not only protect against exacerbating asthma but also promote long-term fitness benefits.
Monitoring Asthma During Exercise
Monitoring asthma during exercise is a critical aspect of ensuring safety and efficacy for individuals with asthma. Engaging in physical activities can offer substantial benefits, but it is paramount to remain vigilant. Asthma can manifest unpredictably, especially during exercise when physical exertion can exacerbate symptoms. Understanding how to monitor and respond to these symptoms significantly enhances the exercise experience and helps prevent complications.
Recognizing Early Symptoms of Asthma Attacks
Recognizing the early symptoms of asthma attacks is vital for individuals engaging in physical activities. Symptoms may include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest tightness. Each of these symptoms can indicate that asthma is becoming severe. The earlier these signs are noticed, the quicker the individual can take action to manage their condition. It is advantageous to develop a personal set of signals that indicate symptom escalation.
Individuals should keep a journal to track symptom patterns and connect them to specific activities or environments. This record may also help healthcare providers refine treatment plans or modify exercise recommendations.
Strategies for addressing symptoms include:


- Taking a break: Stop the activity immediately if symptoms worsen.
- Using a rescue inhaler: Be sure to have a rescue inhaler accessible during exercise to alleviate symptoms swiftly.
- Deep breathing techniques: Practicing controlled breathing can also help manage escalating symptoms.
Using Peak Flow Meters
Using peak flow meters is an effective way to monitor asthma during exercise. These handheld devices measure how well air moves out of the lungs, providing a clear indication of lung function. Regular use of a peak flow meter can help individuals identify their baseline lung function. Once the baseline is known, any significant dip can signal the need for precautions.
The process involves:
- Taking a deep breath and inserting the device mouthpiece.
- Exhaling as forcefully as possible into the peak flow meter.
- Recording the highest number achieved over a series of tests.
Individuals should ideally conduct these assessments in the morning and evening or according to a healthcare professional’s advice. Awareness of day-to-day variations in lung function can aid in recognizing patterns and preventing severe asthma attacks during exercise.
Regular monitoring with a peak flow meter increases confidence and provides clarity regarding lung health and exercise readiness.
In summary, monitoring asthma during exercise cannot be overstated. Recognizing symptoms early and utilizing tools like peak flow meters are essential steps. These actions empower individuals to exercise safely while managing their condition effectively.
Long-Term Strategies for Asthma Management through Exercise
Long-term strategies for asthma management through exercise are crucial for individuals dealing with this condition. Engaging in regular physical activity can enhance lung function, improve overall health, and contribute to better control of asthma symptoms. Establishing a consistent workout routine does more than just promote physical health; it also empowers individuals to manage their asthma more effectively in daily life.
Building Endurance Gradually
One of the most effective approaches to managing asthma while exercising involves building endurance gradually. This method allows the body to adapt to increased levels of exertion over time without triggering asthma symptoms.
To achieve this, set realistic goals that focus on gradual improvement rather than quick results. Start with short, low-intensity workouts, such as a ten-minute walk or gentle cycling. As your body acclimates, gradually extend the duration and intensity of your workouts. This approach can minimize the occurrence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, a common issue for asthmatics. Here are key steps to consider:
- Start Slow: Begin with low-intensity activities appropriate for your current fitness level.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any asthma symptoms during and after exercise. Note patterns that may help you adjust future workouts.
- Increase Gradually: Aim to increase workout duration or intensity no more than 10 percent each week to avoid overexertion.
Incorporating Regular Assessments and Adjustments
Regular assessments and adjustments are fundamental to an effective long-term exercise strategy for asthma management. This process helps to identify what works best for each individual while addressing potential issues that might arise over time.
Consider the following aspects:
- Routine Check-ups: Regularly consult with healthcare professionals to assess your lung function, medication needs, and fitness status.
- Review Goals: Every few months, reassess your fitness goals. These should evolve based on your improvements and any changes in your asthma condition.
- Modify Workouts: Be prepared to adjust your workout routine based on environmental factors, personal experiences, and medical advice. For instance, if outdoor air quality is poor, consider indoor exercise options like a treadmill or stationary bike.
"The only way to keep managing asthma effectively is to stay connected with your healthcare provider and remain adaptable in your exercise plans."
By following these long-term strategies, individuals with asthma can create a sustainable exercise routine that minimizes risks while maximizing benefits. Regular assessments and a gradual approach to building endurance are key components of a comprehensive management plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Exercise and Asthma
Asthma management through exercise is a critical area of concern for individuals living with this condition. This section addresses common inquiries that arise regarding asthma and physical activity. Understanding these questions can empower patients and caregivers to make informed choices. Furthermore, it can clarify misconceptions and highlight the feasibility of incorporating exercise in daily routines enven when asthma is a consideration.
Can Everyone with Asthma Exercise?
While asthma does impose certain limitations, it does not universally prevent individuals from engaging in regular exercise. Most people with asthma can participate in physical activities, provided they follow medical advice and adopt appropriate strategies. The key lies in understanding personal triggers and symptoms.
A discussion with a healthcare provider can yield tailored recommendations. These may include specific types of exercises that suit the individual’s condition. Ensuring an awareness of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction helps in taking preventive measures. The proper approach can transform exercise from a potential risk into a beneficial practice.
What Types of Sports are Best?
Different sports and activities suit individuals based on their asthma severity and trigger factors. Generally, low-impact, aerobic exercises like swimming, cycling, and brisk walking are often recommended. These activities help to build endurance without placing excess strain on the respiratory system.
Some examples of suitable sports include:
- Swimming: The warm, humid air is less likely to induce asthma symptoms. This environment is beneficial for lung function.
- Cycling: This activity allows for easier pacing, offering control over intensity.
- Walking: Simple yet effective, walking can be performed anywhere and tailored to individual fitness levels.
- Yoga: Focuses on controlled breathing and gentle movements, enhancing lung capacity without shock to the system.
What Precautions Should Be Taken?
Taking specific precautions is crucial for asthma sufferers to engage safely in physical activity. Recommended strategies include:
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Gradual warm-up helps prepare the body and respiratory system, while cool-down aids in recovery.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Always consider environmental factors, such as cold air, pollen, or high pollution levels. Choose indoor activities when outdoor conditions are poor.
- Use Medication as Prescribed: Keep reliever inhalers handy when exercising. Always follow the physician’s guidelines regarding pre-exercise medication.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be vigilant of any unusual signs during physical activity. Understanding one’s personal limits ensures safety during workouts.



